From Asa Gray 4 November 1856
Summary
Outlines the ranges of northern U. S. species common to Europe. Hopes to investigate the resemblances between the floras of the north-eastern U. S. and western Europe. Discusses routes by which alpine plants appear to have reached U. S.
| Author: | Asa Gray |
| Addressee: | Charles Robert Darwin |
| Date: | 4 Nov 1856 |
| Classmark: | DAR 165: 95 |
| Letter no: | DCP-LETT-1982 |
Matches: 7 hits
- … In his letter to Asa Gray, 24 August [1856] , CD had indicated that he considered the …
- … to range northwards (see letter to Asa Gray, 12 October [1856] ). When he received the …
- … in the margin, ‘dele’. Letter to Asa Gray, 12 October [1856] , in which CD referred to the …
- … which the introduced species belonged (see letter to Asa Gray, 12 October [1856] ). A. …
- … Gray 1856a . See letter to Asa Gray, 12 October [1856] , n. 6. Gray refers …
- … Dalton Hooker with his own letter to J. D. Hooker, 18 November [1856] . …
- … D. Hooker] 1856, a review of A. de Candolle 1855 . CD forwarded Gray’s letter to Joseph …
From Asa Gray [c. 24 May 1857]
Summary
Discusses difficulties involved in deciding which genera are protean in the light of some comments by H. C. Watson.
| Author: | Asa Gray |
| Addressee: | Charles Robert Darwin |
| Date: | [c. 24 May 1857] |
| Classmark: | DAR 165: 97 |
| Letter no: | DCP-LETT-2104 |
From Asa Gray 7 July 1857
Summary
Believes, with CD, that extinction may be an important factor in explaining plant distributions, but sees no reason why the several species of a genus must ever have had a common or continuous area. "Convince me of that, or show me any good grounds for it … and I think you would carry me a good way with you". It is just such people as AG that CD has to satisfy and convince.
Feels that the crossing of individuals is important in repressing variation and perhaps in perpetuating the species, but instances some plants in which it cannot, apparently, take place.
| Author: | Asa Gray |
| Addressee: | Charles Robert Darwin |
| Date: | 7 July 1857 |
| Classmark: | DAR 205.9: 381; DAR 165: 98 |
| Letter no: | DCP-LETT-2120 |
From Asa Gray 23 September 1856
Summary
Plants that are social in the U. S. but are not so in the Old World.
Distribution of U. S. species common to Europe.
Gives Theodor Engelmann’s opinion on the relative variability of indigenous and introduced plants and notes the effects of man’s settlement on the numbers and distribution of indigenous plants.
| Author: | Asa Gray |
| Addressee: | Charles Robert Darwin |
| Date: | 23 Sept 1856 |
| Classmark: | DAR 165: 94 |
| Letter no: | DCP-LETT-1959 |
From Asa Gray 16 February 1857
Summary
Discusses the ranges of alpine species in U. S. and considers the possible migration routes of such species from Europe.
Lists those U. S. genera which he considers protean and describes the U. S. character of some genera which are protean in Europe.
Describes how he distinguishes introduced and aboriginal stocks of the same species.
| Author: | Asa Gray |
| Addressee: | Charles Robert Darwin |
| Date: | 16 Feb 1857 |
| Classmark: | DAR 165: 96 |
| Letter no: | DCP-LETT-2053 |
From Asa Gray 1 June 1857
Summary
Comments on species with disjoined ranges; does not feel, despite CD’s expectations, that they tend to belong to small families.
Gives the proportion of U. S. trees in which the sexes are separate [see Natural selection, p. 62].
| Author: | Asa Gray |
| Addressee: | Charles Robert Darwin |
| Date: | 1 June 1857 |
| Classmark: | DAR 8: 47bA |
| Letter no: | DCP-LETT-2098 |
From Asa Gray [before 3 April 1858]
| Author: | Asa Gray |
| Addressee: | Charles Robert Darwin |
| Date: | [before 3 Apr 1858] |
| Classmark: | DAR 165: 103 |
| Letter no: | DCP-LETT-2249 |
From Asa Gray 22 May 1855
| Author: | Asa Gray |
| Addressee: | Charles Robert Darwin |
| Date: | 22 May 1855 |
| Classmark: | DAR 106: D1–D2 |
| Letter no: | DCP-LETT-1685 |
Matches: 2 hits
- … letter to Asa Gray, 25 April [1855] . The list, with Asa Gray’s remarks written on it, is in DAR 46.2 (ser. 2): 36. A revised edition of A. Gray 1848 was published in 1856. …
- … 1856 is in the Darwin Library–CUL. An allusion to Joseph Dalton Hooker’s proclivity for ‘lumping’ together plants that other botanists might consider separate species. In his letter …
From Asa Gray [27 and 29 August] and 2 September [1861]
Summary
Gives some observations on the sensitivity of Drosera species and comments on cases of "dioecio-dimorphism".
| Author: | Asa Gray |
| Addressee: | Charles Robert Darwin |
| Date: | 27 and 29 Aug 1861 and 2 Sept 1861 |
| Classmark: | DAR 110 (ser. 2): 76 |
| Letter no: | DCP-LETT-3242 |
From Asa Gray [10 July 1860]
Summary
Cases of "dioecio-dimorphism" as in primroses are widespread. AG always considered them the first step toward bisexuality.
| Author: | Asa Gray |
| Addressee: | Charles Robert Darwin |
| Date: | [10 July 1860] |
| Classmark: | DAR 110 (ser. 2): 77 |
| Letter no: | DCP-LETT-2819 |
From Asa Gray 24 July 1865
| Author: | Asa Gray |
| Addressee: | Charles Robert Darwin |
| Date: | 24 July 1865 |
| Classmark: | DAR 165: 148 |
| Letter no: | DCP-LETT-4877 |
From Asa Gray 11 October 1861
Summary
Notes several cases of "dioecio-dimorphism" in different genera; feels the discovery of pollen that will act only on the pistil of another flower is most important. Believes CD should next turn his attention to investigating cases of "precocious fertilisation".
| Author: | Asa Gray |
| Addressee: | Charles Robert Darwin |
| Date: | 11 Oct 1861 |
| Classmark: | DAR 109: 82–3, DAR 110 (ser. 2): 117, DAR 111: 83 |
| Letter no: | DCP-LETT-3282 |
Matches: 1 hit

Darwin in letters, 1856-1857: the 'Big Book'
Summary
In May 1856, Darwin began writing up his 'species sketch’ in earnest. During this period, his working life was completely dominated by the preparation of his 'Big Book', which was to be called Natural selection. Using letters are the main…
Matches: 1 hits
- … On 14 May 1856, Charles Darwin recorded in his journal that he ‘Began by Lyell’s advice writing …

Darwin and Fatherhood
Summary
Charles Darwin married Emma Wedgwood in 1839 and over the next seventeen years the couple had ten children. It is often assumed that Darwin was an exceptional Victorian father. But how extraordinary was he? The Correspondence Project allows an unusually…
Matches: 1 hits
- … Charles Darwin married Emma Wedgwood in 1839 and over the next seventeen years the couple had ten …
Dramatisation script
Summary
Re: Design – Adaptation of the Correspondence of Charles Darwin, Asa Gray and others… by Craig Baxter – as performed 25 March 2007
Matches: 1 hits
- … Re: Design – performance version – 25 March 2007 – 1 Re: Design – Adaptation of the …

Origin
Summary
Darwin’s most famous work, Origin, had an inauspicious beginning. It grew out of his wish to establish priority for the species theory he had spent over twenty years researching. Darwin never intended to write Origin, and had resisted suggestions in 1856…
Matches: 1 hits
- … Darwin’s most famous work, Origin, had an inauspicious beginning. It grew out of his wish to …

Six things Darwin never said – and one he did
Summary
Spot the fakes! Darwin is often quoted – and as often misquoted. Here are some sayings regularly attributed to Darwin that never flowed from his pen.
Matches: 1 hits
- … Spot the fakes! Darwin is often quoted – and as often misquoted. Here are some sayings regularly …
Dates of composition of Darwin's manuscript on species
Summary
Many of the dates of letters in 1856 and 1857 were based on or confirmed by reference to Darwin’s manuscript on species (DAR 8--15.1, inclusive; transcribed and published as Natural selection). This manuscript, begun in May 1856, was nearly completed by…
Matches: 1 hits
- … Many of the dates of letters in 1856 and 1857 were based on or confirmed by reference to Darwin’s …
Women’s scientific participation
Summary
Observers | Fieldwork | Experimentation | Editors and critics | Assistants Darwin’s correspondence helps bring to light a community of women who participated, often actively and routinely, in the nineteenth-century scientific community. Here is a…
Matches: 1 hits
- … Observers | Fieldwork | Experimentation | Editors and critics | Assistants …

Descent
Summary
There are more than five hundred letters associated with the research and writing of Darwin’s book, Descent of man and selection in relation to sex (Descent). They trace not only the tortuous route to eventual publication, but the development of Darwin’s…
Matches: 1 hits
- … ‘ Our ancestor was an animal which breathed water, had a swim-bladder, a great swimming …

Species and varieties
Summary
On the origin of species by means of natural selection …so begins the title of Darwin’s most famous book, and the reader would rightly assume that such a thing as ‘species’ must therefore exist and be subject to description. But the title continues, …or…
Matches: 1 hits
- … On the origin of species by means of natural selection …so begins the title of Darwin’s most …

Darwin’s reading notebooks
Summary
In April 1838, Darwin began recording the titles of books he had read and the books he wished to read in Notebook C (Notebooks, pp. 319–28). In 1839, these lists were copied and continued in separate notebooks. The first of these reading notebooks (DAR 119…
Matches: 1 hits
- … In April 1838, Darwin began recording the titles of books he had read and the books he wished to …

Darwin in letters, 1882: Nothing too great or too small
Summary
In 1882, Darwin reached his 74th year Earthworms had been published the previous October, and for the first time in decades he was not working on another book. He remained active in botanical research, however. Building on his recent studies in plant…
Matches: 1 hits
- … In 1882, Darwin reached his 74th year Earthworms had been published the previous October, and …

Before Origin: the ‘big book’
Summary
Darwin began ‘sorting notes for Species Theory’ on 9 September 1854, the very day he concluded his eight-year study of barnacles (Darwin's Journal). He had long considered the question of species. In 1842, he outlined a theory of transmutation in a…
Matches: 1 hits
- … Darwin began ‘sorting notes for Species Theory’ on 9 September 1854, the very day he concluded his …
Scientific Networks
Summary
Friendship|Mentors|Class|Gender In its broadest sense, a scientific network is a set of connections between people, places, and things that channel the communication of knowledge, and that substantially determine both its intellectual form and content,…
Matches: 1 hits
- … Friendship | Mentors | Class | Gender In its broadest sense, a scientific …

Thomas Henry Huxley
Summary
Dubbed “Darwin’s bulldog” for his combative role in controversies over evolution, Huxley was a leading Victorian zoologist, science popularizer, and education reformer. He was born in Ealing, a small village west of London, in 1825. With only two years of…
Matches: 1 hits
- … Dubbed “Darwin’s bulldog” for his combative role in controversies over evolution, Huxley was a …

Darwin in letters, 1863: Quarrels at home, honours abroad
Summary
At the start of 1863, Charles Darwin was actively working on the manuscript of The variation of animals and plants under domestication, anticipating with excitement the construction of a hothouse to accommodate his increasingly varied botanical experiments…
Matches: 1 hits
- … At the start of 1863, Charles Darwin was actively working on the manuscript of The variation of …

Darwin in letters, 1872: Job done?
Summary
'My career’, Darwin wrote towards the end of 1872, 'is so nearly closed. . . What little more I can do, shall be chiefly new work’, and the tenor of his correspondence throughout the year is one of wistful reminiscence, coupled with a keen eye…
Matches: 1 hits
- … ‘My career’, Darwin wrote towards the end of 1872, ‘is so nearly closed. . . What little more I …
4.16 Joseph Simms, physiognomy
Summary
< Back to Introduction In September 1874, the American doctor Joseph Simms, then on a three-year lecture tour of Britain, sent Darwin a copy of his book, Nature’s Revelations of Character; Or, Physiognomy Illustrated. He was seeking a public…
Matches: 1 hits
- … < Back to Introduction In September 1874, the American doctor Joseph Simms, then on a …
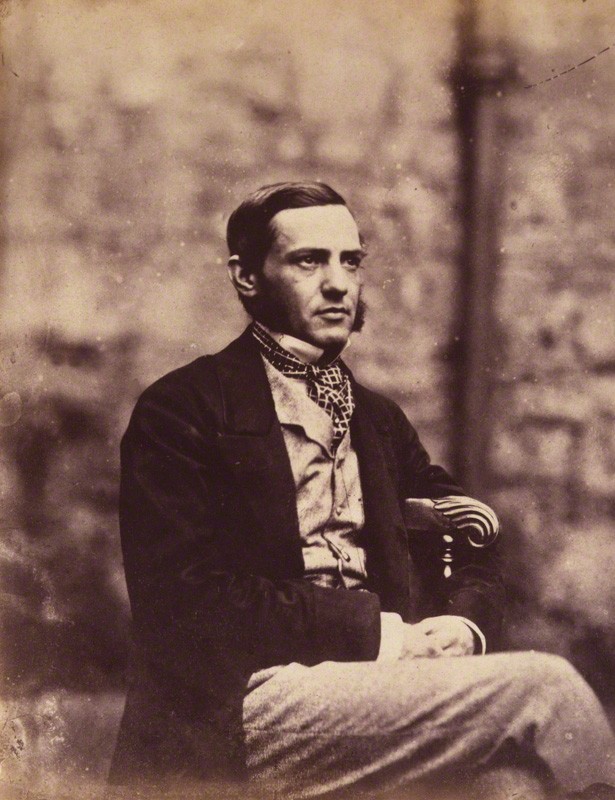

Language: key letters
Summary
How and why language evolved bears on larger questions about the evolution of the human species, and the relationship between man and animals. Darwin presented his views on the development of human speech from animal sounds in The Descent of Man (1871),…
Matches: 1 hits
- … The origin of language was investigated in a wide range of disciplines in the nineteenth century. …

Hermann Müller
Summary
Hermann (Heinrich Ludwig Hermann) Müller, was born in Mühlberg near Erfurt in 1829. He was the younger brother of Fritz Müller (1822–97). Following the completion of his secondary education at Erfurt in 1848, he studied natural sciences at Halle and Berlin…
Matches: 1 hits
- … Hermann (Heinrich Ludwig Hermann) Müller, was born in Mühlberg near Erfurt in 1829. He was the …

Darwin in letters, 1858-1859: Origin
Summary
The years 1858 and 1859 were, without doubt, the most momentous of Darwin’s life. From a quiet rural existence filled with steady work on his ‘big book’ on species, he was jolted into action by the arrival of an unexpected letter from Alfred Russel Wallace…
Matches: 1 hits
- … The years 1858 and 1859 were, without doubt, the most momentous of Darwin’s life. From a quiet …